Crohn's Disease: Symptoms, Causes & When To See A Doctor
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It causes inflammation of your digestive tract, which can lead to abdominal pain, severe diarrhoea, fatigue, weight loss and malnutrition.
Inflammation caused by Crohn's disease can involve different areas of the digestive tract in different people. This inflammation often spreads into the deeper layers of the bowel.
Crohn's disease can be both painful and debilitating and sometimes may lead to life-threatening complications.
While there's no known cure for Crohn's disease, therapies can impressively reduce its signs and symptoms and even bring about long-term remission and healing of inflammation. With treatment, many people with Crohn's disease can function well.
Symptoms of Crohn's Disease
With Crohn's disease, any part of your small or large intestine can be involved, and it may be continuous or may involve multiple segments. In some people, the disease is confined to the colon (a part of the large intestine).
Signs and symptoms of Crohn's disease can range from mild to severe. They often develop gradually, but sometimes will come on suddenly, without warning. You may also have periods when you have no signs or symptoms (this is referred to as remission).
When the disease is active, signs and symptoms may include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Blood in your stool
- Delayed growth or sexual development, in children
- Diarrhoea
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Inflammation of skin, eyes and joints
- Inflammation of the liver or bile ducts
- Iron deficiency (anaemia)
- Kidney stones
- Mouth sores
- Pain or drainage of the anus due to inflammation from a tunnel into the skin (fistula)
- Reduced appetite and weight loss
Causes of Crohn's Disease
The exact cause of Crohn's disease remains unknown. Previously, diet and stress were suspected, but now doctors know these factors may aggravate, but do not cause, Crohn's disease.
Several factors, such as heredity and a malfunctioning immune system, are likely to play a role in its development. See below for more information.
- Heredity. Crohn's is more common in people who have family members with the disease. This suggests genes may play a role in making people more susceptible. However, most people with Crohn's disease don't have a family history of the illness.
- Immune system. It's possible that a virus or bacterium may trigger Crohn's disease; however, scientists have yet to identify such a trigger. When your immune system tries to fight off the invading microorganism, an abnormal immune response causes the immune system to attack the cells in the digestive tract, too.
Risk factors of Crohn's Disease
Risk factors for Crohn's disease may include:
- Age. Crohn's disease can occur at any age, but you're likely to develop the condition when you're young. Most people who develop Crohn's disease are diagnosed before 30.
- Cigarette smoking. Cigarette smoking is the most important controllable risk factor for developing Crohn's disease. Smoking also leads to more-severe diseases and a greater risk of having surgery. If you smoke, it's important to stop.
- Ethnicity. Although Crohn's disease can affect any ethnic group, whites have the highest risk, especially people of Eastern European (Ashkenazi) Jewish descent. However, the incidence of Crohn's disease is increasing among Black people who live in North America and the United Kingdom.
- Family history. You're at higher risk if you have a first-degree relative, such as a parent, sibling or child, with Crohn's disease. As many as 1 in 5 people with Crohn's disease has a family member with the disease.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications. These include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), naproxen sodium (Aleve), diclofenac sodium and others. While they do not cause Crohn's disease, they can lead to inflammation of the bowel which makes Crohn's disease worse.
Complications of Crohn's Disease
Crohn's disease may lead to one or more of the following complications:
- Anal fissure. A small tear in the tissue that lines the anus or in the skin around the anus, where infections can occur. It's often associated with painful bowel movements and may lead to a perianal fistula.
- Blood clots. Crohn's disease increases the risk of blood clots in veins and arteries.
- Bowel obstruction. Crohn's disease can affect the entire thickness of the intestinal wall. Over time, parts of the bowel can scar and narrow, which may block the flow of digestive contents. You may require surgery to remove the diseased portion of your bowel.
- Colon cancer. The Crohn's disease that affects your colon increases your risk of colon cancer. General colon cancer screening guidelines for people without Crohn's disease call for a colonoscopy every 10 years beginning at age 50. Ask your doctor whether you need to have this test done sooner and more frequently.
- Fistulas. Sometimes ulcers can extend completely through the intestinal wall, creating a fistula — an abnormal connection between different body parts. Fistulas can develop between your intestine and your skin, or between your intestine and another organ. Fistulas near or around the anal area (perianal) are the most common kind.
In some cases, a fistula may become infected and form an abscess, which can be life-threatening if not treated.
When fistulas develop in the abdomen, food may bypass areas of the bowel that are necessary for absorption. Fistulas may form between loops of the bowel, in the bladder or vagina, or through the skin, causing continuous drainage of bowel contents to your skin. - Malnutrition. Diarrhoea, abdominal pain and cramping may make it difficult for you to eat or for your intestine to absorb enough nutrients to keep you nourished. It's also common to develop anaemia due to low iron or vitamin B-12 caused by the disease.
- Medication risks. Certain Crohn's disease drugs that act by blocking functions of the immune system are associated with a small risk of developing cancers such as lymphoma and skin cancers. They also increase the risk of infection.
Corticosteroids can be associated with a risk of osteoporosis, bone fractures, cataracts, glaucoma, diabetes and high blood pressure, among other conditions. Work with your doctor to determine the risks and benefits of medications. - Other health problems. Crohn's disease can cause problems in other parts of the body. These include anaemia, skin disorders, osteoporosis, arthritis, and gallbladder or liver disease.
- Ulcers. Chronic inflammation can lead to open sores (ulcers) anywhere in your digestive tract, including your mouth and anus, and in the genital area (perineum).
When to see a doctor
See your doctor if you have persistent changes in your bowel habits or if you have any of the signs and symptoms of Crohn's disease, such as:
- Abdominal pain
- Blood in your stool
- Nausea and vomiting
- Ongoing bouts of diarrhoea that don't respond to over-the-counter medications
- Unexplained fever lasting more than a day or two
- Unexplained weight loss
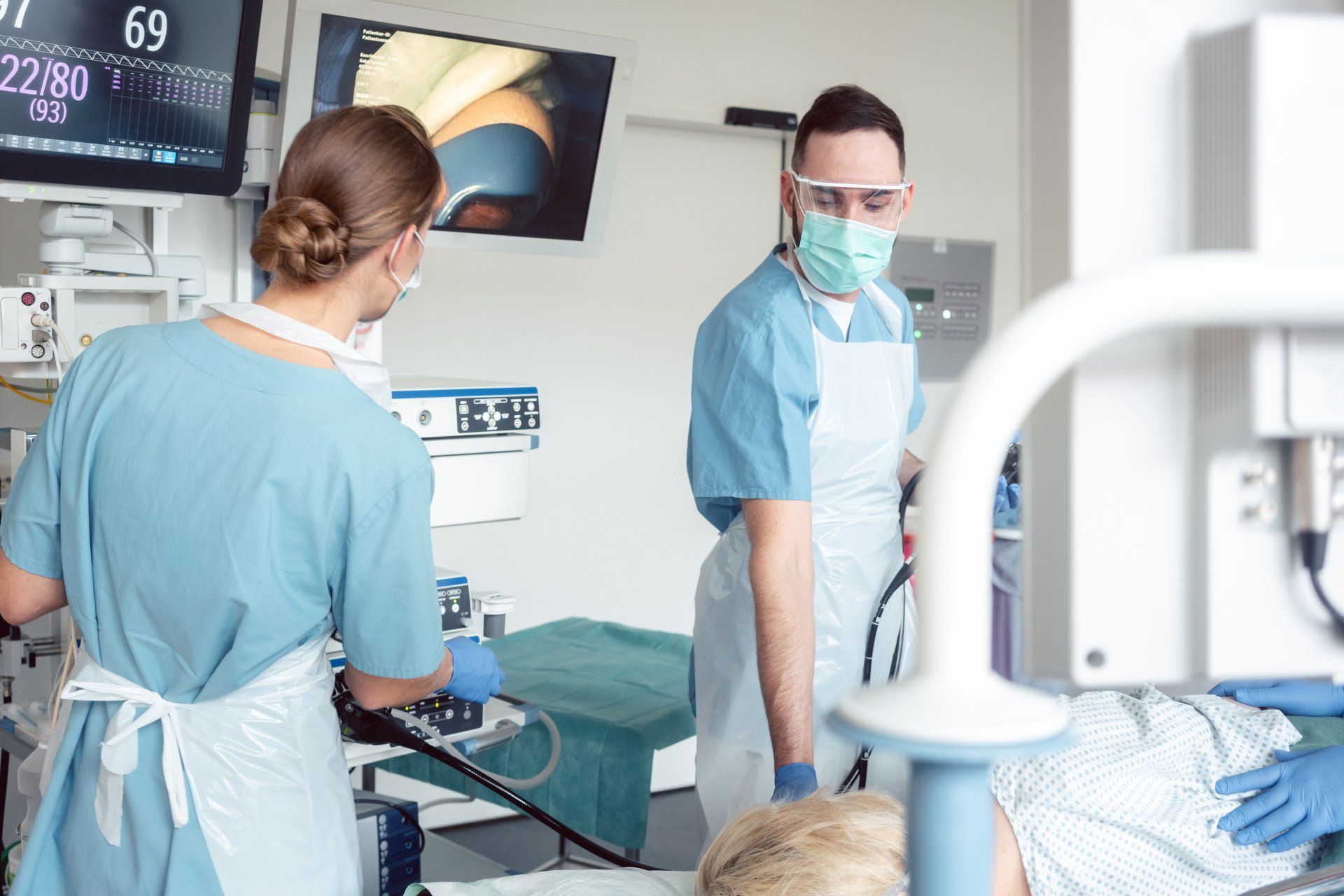
How We Can Help
The Chartwell Hospital specialises in helping restore people to optimal digestive health. We are conveniently located in London with a facility dedicated to providing high-quality endoscopic and colonoscopic services in a comfortable, welcoming environment. Our team of specialists can provide compassionate, personalised care and will work with you to diagnose the problem, review your options and choose the treatment that best suits you. To book a FREE consultation please use our online form to arrange a date and time that works best for you.