Patients
Services
About Us
How Can We Help
Consultants
Get in touch
01702 782005
Unlocking Optimal Health: Understanding Macronutrients for Wellness and Nutrition Balance
When it comes to nutrition, many of us focus on counting calories. But is this the best approach to achieve optimal health and wellness?
The answer is no.
Calorie counting alone can be misleading. It doesn't consider the quality of the calories consumed and the foods chosen.
Macronutrient tracking and balancing is method that goes beyond mere calorie counting. It focuses on the types of nutrients we consume, namely proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. These macronutrients play crucial roles in our bodies. They provide energy, support growth and repair, and maintain various bodily functions. Understanding and tracking these macronutrients can lead to more balanced and nutritious eating habits.

In this guide, we'll delve into the world of macronutrient tracking and balancing. We'll explore each macronutrient, their roles, and how to create a balanced meal plan. Whether you're a fitness enthusiast or someone looking to improve dietary habits, this guide is for you.
Understanding Macronutrients
Before we dive into tracking and balancing, let's first understand what macronutrients are.
Macronutrients are the nutrients our bodies need in large amounts for energy provision that account for daily calorie intake.. They include proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Each of these macronutrients provides us with energy, measured in calories. However, they are not just about energy. They also perform various vital functions in our bodies and their requirements can vary widely depending on several factors such as age, body weight, physical activity levels and underlying health conditions. Understanding these roles can help us make better dietary choices.
The Roles of Protein, Carbohydrates, and Fats
Protein is often referred to as the body's building block. It's crucial for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues.Protein also plays a role in hormone production and immune function. Sources of protein include non vegetarian foods like chicken (without skin), fish, eggs and vegetarian proteins dairy, pulses and lentils.
Carbohydrates are the body's main source of energy. They fuel our brains, kidneys, heart muscles, and the central nervous system.
Carbohydrates can be simple or complex, affecting how quickly they're digested and absorbed. Sources of carbohydrates include cereal & grains, fruits, vegetables and dairy products.
Fats, often misunderstood, are essential for our bodies. They provide energy, support cell growth, and help protect our organs.Fats also play a crucial role in nutrient absorption and hormone production. Sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Understanding these macronutrients and their roles is the first step towards better nutrition. Next, we'll explore how to track and balance these macronutrients for optimal health.
The Limitations of Calorie Counting
Calorie counting has been a popular method for managing weight. However, it has its limitations. While it's true that consuming fewer calories than we burn can lead to weight loss, not all calories are created equal.
A calorie from a doughnut is not the same as a calorie from an avocado. The former is high in sugar and lacks nutrients, while the latter is packed with healthy fats, vitamins and fibre. Simply counting calories can lead to nutrient deficiencies and poor health.
It also doesn't consider the different roles and effects of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats in our bodies.
That's where macronutrient tracking comes in. It goes beyond calorie counting to ensure we're not just eating the right amount, but also the right kind of food. Mindfully choosing whole foods, lean protein choices, healthy fats and variety of vegetables & fruits over processed foods could have a significant impact in reducing excessive salt, fats and preservatives that helps to avoid weight gain and inflammation in the body.
In the next section, we'll explore how to track your macronutrients.
How to Track Your Macronutrients
Tracking macronutrients involves more than just counting calories. It requires understanding the roles of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats in our bodies.
Each of these macronutrients provides a different amount of energy. Proteins and carbohydrates provide 4 calories per gram, while fats provide 9 calories per gram. Knowing this, you can calculate your macronutrient needs based on your daily calorie intake.
Calculating Your Macronutrient Needs
To calculate your macronutrient needs, you first need to determine your daily calorie intake. Calorie requirements are calculated by estimating individual energy needs known as Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), which is multiplied with your physical activity level.
However, this can be done using online calculators that consider factors like age, sex, weight, height, and activity level.
Once you know your daily calorie intake, you can distribute it among proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
Setting Your Macronutrient Ratios
The distribution of calories among macronutrients is often expressed as a ratio.
For example, a common ratio for weight loss would be about 45% carbohydrates, 30% proteins, and 25 % fats.
This ratio can be adjusted based on your health goals and individual needs. Remember, these ratios are not set in stone and can be tweaked as you progress.
In the next section, we'll look at some tools that can help you track your macronutrients.
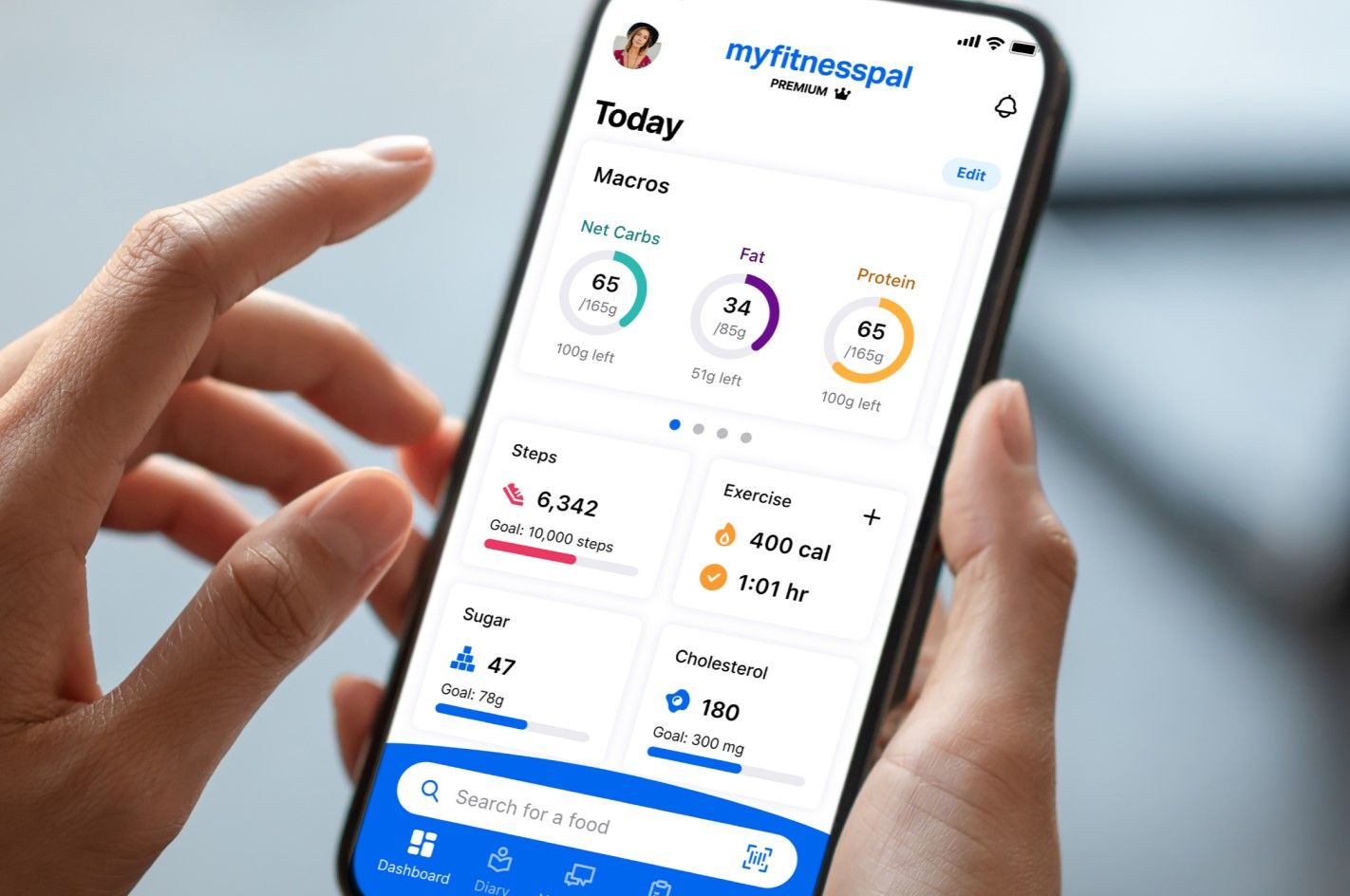
Tools for Macronutrient Tracking
In the digital age, tracking macronutrients has become easier than ever.
There are numerous apps and online tools that can help you log your food intake and monitor your macronutrient balance.
These tools can provide valuable insights into your eating habits and help you make informed dietary decisions.

Popular Food Tracking Apps
One popular food tracking app is MyFitnessPal. It has a vast food database and allows you to set custom macronutrient goals.
Another option is Cronometer, which provides detailed nutrition information and tracks both macronutrients and micronutrients.
Choosing the right tool can make macronutrient tracking a seamless part of your daily routine.
Balancing Macronutrients in Your Diet
Balancing macronutrients in your diet is not a one-size-fits-all process.
It requires understanding your individual needs and goals.
For instance, someone aiming for weight loss might have a different macronutrient ratio compared to someone building muscle.
It's also important to remember that balance doesn't mean equal portions.
Each macronutrient has a different role in the body and may be needed in different amounts.
Macronutrient Ratios for Different Goals
Nevertheless, the fundamental element of diets for weight loss and its maintenance is creating an energy deficit. Research indicates that proteins increase the feelings of fullness more than equivalent amounts of carbohydrates or fat, highlighting its role in promoting satiety and potentially aiding in weight management and promoting a healthier body composition.
A macronutrient ratio for weight loss around 45% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 25% fat ensures you're getting enough protein to maintain muscle mass while still providing sufficient energy from carbohydrates and fats.
Some low carbohydrate diets may initially greatly restrict carbohydrate intake in the early phase, gradually allowing for more carbohydrates over time as the diet progresses. However, it is important to consider individual dietary needs and goals when determining the appropriate carbohydrate intake within a balanced diet plan. Based on current evidence, in the short term, high protein, low-carbohydrate diets and intermittent fasting may promote greater weight loss and could be considered as a jumpstart for some individuals. Caution is advised due to the potential adverse effects associated with severe low calorie dietary approaches. In the long term, research suggests that various diets can lead to similar weight loss outcomes, with adherence to the chosen diet being the key predictor of success.
Adjusting Intake Based on Progress
Monitoring your progress is key when balancing macronutrients.
Remember, it's not just about the numbers. Listen to your body and adjust your intake based on how you feel and perform.
Balancing macronutrients is a dynamic process that can be fine-tuned as you go along.
The Importance of Macronutrient Quality
While tracking macronutrients, it's crucial to consider the quality of your food sources.
Not all proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are created equal.
Incorporating lean proteins like chicken (without skin), fish, eggs and vegetarian proteins like chickpeas, baked beans, green peas, varieties of lentils and low-fat dairy like milk, yogurt, cottage cheese, tofu etc can significantly contribute to satiety in a weight loss plan. It is advisable to consume red meats (beef, lamb, pork, venison), organ meats & processed meats less frequently due to high fat & sodium content and potential adverse effects on blood cholesterol levels. Avoid processed meats, which can be high in unhealthy fats and sodium.
When it comes to carbohydrates, choose complex carbs like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. These provide more nutrients and fiber compared to simple carbs found in sugary foods and drinks. Complex carbohydrates like whole grains like quinoa, buck wheat, brown rice, corn and lentils, potatoes & sweet potatoes, supplies nutrients & sufficient fibre that provides satiety and greater control of blood sugars & cholesterol values. Whilst simple carbohydrate sources like sugars, cookies, and pastries tend to be "empty calories," (providing only calories apart from nutrients) easily lead to weight gain and increase in overall fat.
Lastly, focus on healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
Replacing saturated fats like butter with monounsaturated fats found in plant oils like olive, avocado and including polyunsaturated fats like omega-3 fats in oily fish like salmon, tuna, sardine, mackerel, anchovies and walnuts, chia seeds & flax seeds would be ideal choices for healthy fats. Avoid trans fats and limit saturated fats, which can increase your risk of heart disease.
Remember, the quality of your macronutrients can significantly impact your overall health and wellness.
Meal Planning with Macronutrients in Mind
Meal planning is a practical way to ensure you're meeting your macronutrient goals. It involves planning your meals and snacks ahead of time based on your individual macronutrient needs.
To start, determine the number of meals and snacks you'll have each day. Then, divide your daily macronutrient goals across these meals and snacks. This can help ensure a steady supply of energy throughout the day and prevent overeating.
Here are some tips for meal planning with macronutrients in mind:
- Include a source of protein, carbohydrates, and fats in each meal.
- Use a food tracking app to help plan and adjust your meals.
- Prepare meals in advance to save time and ensure you stick to your plan.
- Be flexible and adjust your plan as needed based on your hunger, fullness, and other factors.

Sample Meal Plan
Here's an example of a meal plan might look like for someone with a daily goal of 150g protein, 200g carbohydrates, and 70g fats:
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach and whole grain toast(30g protein, 40g carbohydrates, 15g fats)
Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with quinoa and avocado(40g protein, 50g carbohydrates, 20g fats)
Afternoon Snack: Greek yogurt with berries and almonds(20g protein, 30g carbohydrates, 10g fats)
Dinner: Baked salmon with sweet potato and broccoli(40g protein, 50g carbohydrates, 15g fats)
Evening Snack: Cottage cheese with apple slices and peanut butter(20g protein, 30g carbohydrates, 10g fats)
This plan provides a balance of macronutrients at each meal and snack.
Remember,this is just an example and your meal plan may look different based on your individual needs and preferences.
The key is to find a balance that works for you and supports your health goals.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Macronutrient Tracking
Macronutrient tracking can be a powerful tool for improving your nutrition. However, it's not without its challenges.
One common issue is the time and effort required to track your food intake accurately. This can be especially difficult when eating out or cooking complex meals at home. A solution to this is to use a food tracking app that has a large database of foods and allows you to save meals and recipes for easy tracking.
Another challenge is the potential for becoming overly focused on numbers, which can lead to stress and unhealthy eating behaviours. It's important to remember that macronutrient tracking is a tool to help you understand your eating habits and make positive changes. It's not meant to be a strict rule or cause anxiety. If you find yourself becoming too obsessed with tracking, it may be helpful to take a break or seek guidance from a registered dietitian or nutritionist.
The Psychological Impact of Macronutrient Tracking
Macronutrient tracking can have a significant psychological impact. On one hand, it can increase dietary awareness and control, leading to improved eating habits and health outcomes.
On the other hand, it can also lead to obsession or disordered eating patterns in some individuals. It's crucial to approach macronutrient tracking with a balanced mindset, focusing on overall health and well-being rather than striving for perfection. If tracking becomes a source of stress or anxiety, it may be beneficial to seek support from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.
Long-Term Benefits of Macronutrient Awareness
Understanding and tracking your macronutrients can have numerous long-term benefits. It can lead to more balanced and nutritious eating habits, which can improve overall health and well-being.
By focusing on macronutrients, you can ensure that your body is getting the necessary nutrients it needs to function optimally. This can lead to increased energy levels, improved physical performance, better mood and cognitive function, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Moreover, macronutrient awareness can also support weight management goals. Whether you're looking to lose weight, gain muscle, or maintain your current weight, understanding your macronutrient intake can help you make informed dietary decisions to support these goals. It's a sustainable approach to nutrition that can lead to long-lasting changes and improvements in your health.
Conclusion
Balancing macronutrients in your diet is a personalised process that requires understanding your unique needs and goals. Whether you're aiming for weight loss, muscle gain, or simply overall wellness, adjusting your macronutrient ratios can help you achieve your desired outcomes. It's essential to listen to your body, monitor your progress, and make adjustments as needed to ensure you're fueling your body optimally. Remember, balance is key, and finding the right macronutrient ratio for you can lead to improved energy levels, physical performance, and overall health.
If you would like to find out more about how we can help you lose weight with a gastric balloon, check out our weight loss section
HERE